Introduction
In general, the category of Aronia was divided by 3 different color such as Aronia arbutifolia (red chokeberry), Aronia prunifolia (purple chokeberry), and Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry (Kokotkiewicz et al., 2010; Borowska and Brzoska, 2016; Kim et al., 2018). Especially Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) was cultivated for medicine use in the former Soviet Union from the middle of the 20th century, hence researchers had a focus on Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) (Borowska et al., 2017; Sic Zlabur et al., 2017; Kim et al., 2018).
Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) had much amounts of phenolic components than those of the other berries (Chrubasik, et al., 2010; Kim et al., 2018). And the products of Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) were sold the form of powder (Chrubasik, et al., 2010; Kim et al., 2018). Hence, it could be directly applied for adding Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) to dairy products for upgrading nutritional quality and sensory attributes (Nguyen and Hwang, 2016; Jurikova et al., 2017; Kim et al., 2018).
Then, the ultimate goal of this study was to manufacture market milk, Yogurt and Kefir the bioactive Yogurt added with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder for improving sensory attributes. In this experiment, among various physicochemical characteristics of dairy products, sensory attributes of market milk, Yogurt and Kefir added with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder were analyzed.
Materials and Methods
The power type of Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) was produced in Kiantama OY (Finland), and also was the food additive grade used in this study.
The powder of Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) was added to market milk (Seoul Dairy Co-op, Korea) at concentrations of 0% (control), 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%, respectively, and then mixed thoroughly (T 25 digital ULTRA-TURRAX®, IKA-Labortechnik, Germany). Then, the market milk with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder was kept at 4±0.5°C.
According to the instruction given by Kim et al. (2017), Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder was added to Yogurt premix at concentrations of 0% (control), 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%, and then mixed thoroughly. In this study, a ready-mixed starter culture (Lyofast YAB 450AB, Sacco srl., Codaragok, Italy) consisted of Streptococcus thermophiles, Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, and Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis was artificially inoculated and then fermented at 42±1°C for 5 h. The Yogurt was kept at around 4±0.5°C for 24 h (Fig. 1).
According to the instruction given by Kim et al. (2017), Kefir was manufacture by Kefir grains obtained from Center for KU Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University in Seoul, Korea. Then Kefir samples were added with different concentration of Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%). The final Kefir products were cooled at 4°C and then stored in a refrigerator.
The sensory attributes was analyzed by 15 trained panelists between 20 and 50 years of age who gave written informed consent after explanation of risk-benefits of participation prior to the study. The samples was randomly served in single-use plastic cups (10±1 mL) about 8±1°C. All assessors completed a test assessment form to compare the 5 different sensory attributes - (1) taste, (2) color, (3) flavor, (4) texture and (5) overall acceptability - by a 5-point hedonic scale (1 as extremely poor; 2 as poor; 3 as fair; 4 as good; and 5 as excellent).
Statistical analysis was performed by GraphPad Prism 5.0 (GraphPad Softward Inc., San Diegeo, CA, USA), and statistical significance was considered at p<0.05. In this study, all data were showed as means±standard deviation which were performed by two separate experiments with triplicate assays.
Results and Discussion
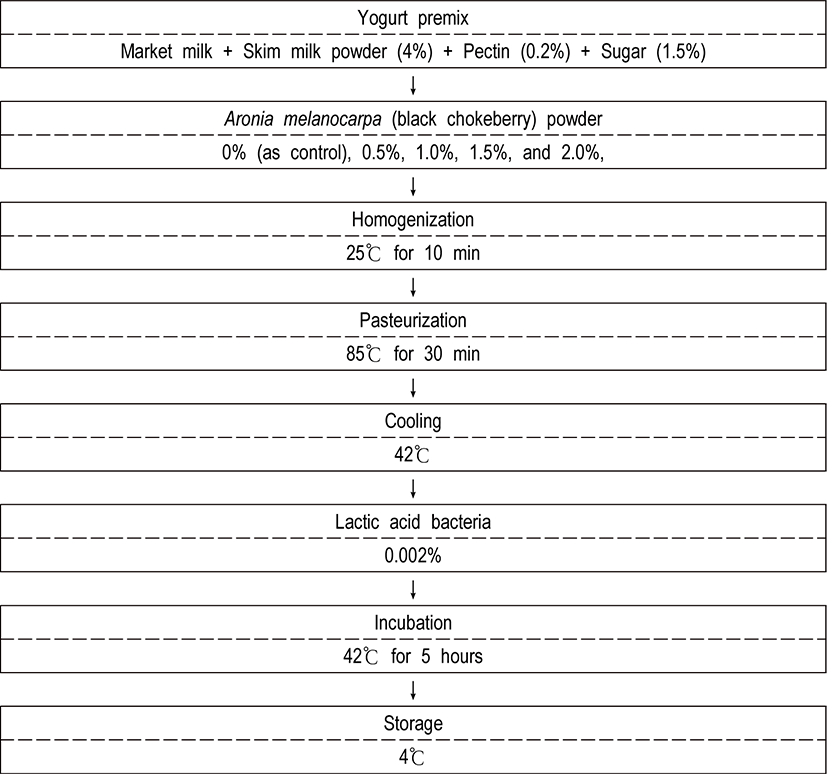
The market milk was prepared with addition of Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder at concentrations of 0% (as control), 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%, respectively, and the results were summarized in Fig. 2.
According to statistical analysis of the sensory attributes, there was statistical difference in taste, color, flavor, texture and overall acceptability between treated group and control group (p<0.05).
The scores of taste in market milk with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) showed 4.2, 3.3, 2.8, 2.77, and 2.55, respectively. The scores of color in market milk with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) showed 4.2, 2.7, 2.3, 1.7, and 1.6, respectively. The scores of flavor in market milk with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) showed 4.3, 3.6, 3.4, 3.3, and 3.2, respectively. The scores of texture in market milk with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) showed 4.1, 3.0, 2.9, 2.8, and 2.7, respectively. And the scores of overall acceptability in market milk with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) showed 4.23, 3.16, 2.89, 2.66, and 2.53, respectively.
Consequently, among the treated group compared with the control group (0%), the scores of taste, flavor, texture and overall acceptability were the same or lower in Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder-containing market milk with 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2%.
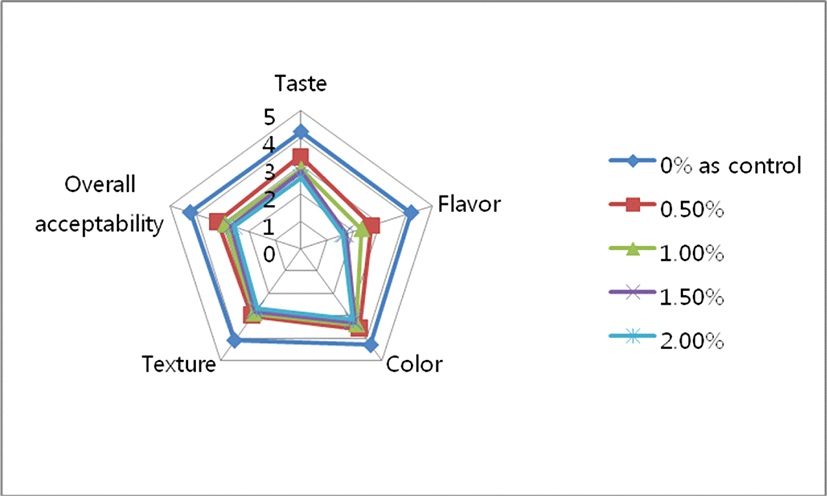
The Yogurt was prepared with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder at concentrations of 0% (as control), 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%, respectively, and the results were summarized in Fig. 3.
The scores of taste in Yogurt with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (0.5%,
1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) ranged from 4.11 points to 3.33 point, which were lower than those for Yogurt added with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%) (4.33 points). The scores of color in Yogurt with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) ranged from 4.3 points to 3.8 point, which was comparable to that of Yogurt added with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%) showed 4.3 points. The scores of flavor in Yogurt with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) ranged from 4.1 points to 3.9 point, whereas that of Yogurt added with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%) showed 4.2 points. The scores of texture in Yogurt with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) ranged from 4.2 points to 3.6 point, whereas that of Yogurt added with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%) showed 4.3 points. The scores of overall acceptability in Yogurt with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) ranged from 4.2 points to 3.7 point, whereas that of Yogurt added with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%) showed 4.3 points. Consequently, the sensory attributes decreased with increasing amounts of added Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder. Among the treated group, the high scores were received by Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder-containing Yogurt with 0.5%, 1.0%, and 1.5% compared with the control group (0%).
To summarize the results of this study, the scores of taste, flavor, color, and overall acceptability decreased in proportion to the added amount of Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder.
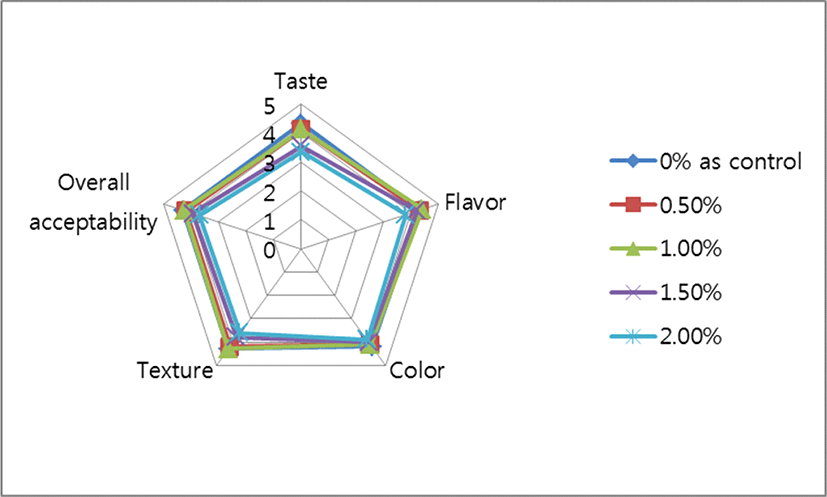
Kefir was prepared with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder at concentrations of 0% (as control), 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%, respectively, and the results were summarized in Fig. 4.
According to statistical analysis of the sensory attributes, there was not any statistical difference in color and flavor, but in taste, texture and overall acceptability between control group and treated group (p<0.05).
The scores of taste in Kefir with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) showed 3.88, 3.77, 3.55, 3.44, and 3.22, respectively. The scores of color in Kefir with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) showed 4.3, 4.2, 4.0, 3.9, and 3.7, respectively. The scores of flavor in Kefir with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) showed 3.9, 3.6, 3.5, 3.6, and 3.5, respectively. The scores of texture in Kefir with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) showed 4.2, 4.0, 3.8, 3.7, and 3.3, respectively. And the scores of overall acceptability scores in Kefir with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder (control as 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%) showed 4.1, 3.92, 3.74, 3.69, and 3.45, respectively. Consequently, among the treated group compared with the control group (0%), the scores of taste, flavor, texture and overall acceptability were the same or lower in Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder-containing Kefir with 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2%.
In general, since Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) had a astringent taste in itself, more than 3% Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) juice could not be used for making various dairy products including Yogurt (Nguyen and Hwang, 2016). According to a study by Nguyen and Hwang (2016), they reported that there were not any statistical differences in several sensory attributes between yogurt added with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) and normal yogurt (control as 0%). the results of this study showed a similar tendency in previous study (Nguyen and Hwang, 2016).
Therefore, future studies will need to find out not only how to maintain a good sensory attributes of various dairy products added with Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) powder, but also how to improve human health.






